초록
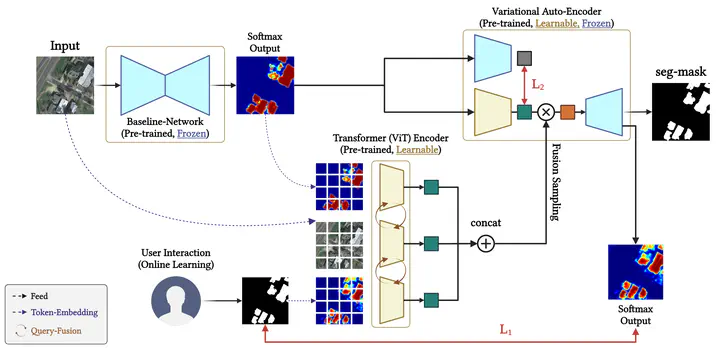
Over the past few decades, geospatial objects have been extensively recognized as significant components in remote sensing applications, including environmental monitoring, urban planning, and defense. Particularly, accurate segmentation of objects has aimed at meaningful observations from aerial imagery, leading to the necessity of deep learning-based methodologies. However, conventional deep learning-based segmentation methodologies exhibit limited generalization capabilities across diverse geographical domains due to inherent variations in regional characteristics and data distribution shifts. Furthermore, most existing approaches strongly rely on static, pre-trained models lacking the adaptability to handle previously unseen data. To alleviate these limitations, we propose a novel Few-shot Semi-Online Adaptation framework incorporating interactive user feedback to iteratively refine segmentation outputs. By leveraging online learning and test-time adaptation, our approach enables models to continuously be accurate based on minimal user corrections, ensuring flexibility and adaptability to new environments. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively enhances the segmentation accuracy with minimal user intervention, bridging the gap between automated segmentation and domain-specific expertise. Our research contributes to the development of interactive, user-adaptive segmentation models to facilitate geospatial analysis more efficiently and reliably.