Publication
Federated Learning for Thyroid Ultrasound Image Analysis to Protect Personal Information: Validation Study in a Real Health Care Environment
Haeyun Lee, Young Jun Chai, Hyunjin Joo, Kyungsu Lee, Jae Youn Hwang, Seok-Mo Kim, Kwangsoon Kim, Inn-Chul Nam, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Myeong-Chul Lee, Hiroo Masuoka, Akira Miyauchi, Kyu-Eon Lee, Sung-Wan Kim, and Hyoun-Joong Kong. "Federated Learning for Thyroid Ultrasound Image Analysis to Protect Personal Information: Validation Study in a Real Health Care Environment," Journal of Medical Internet Research Medical Informatics (JMIR Medical Informatics) , 2021.
Abstract
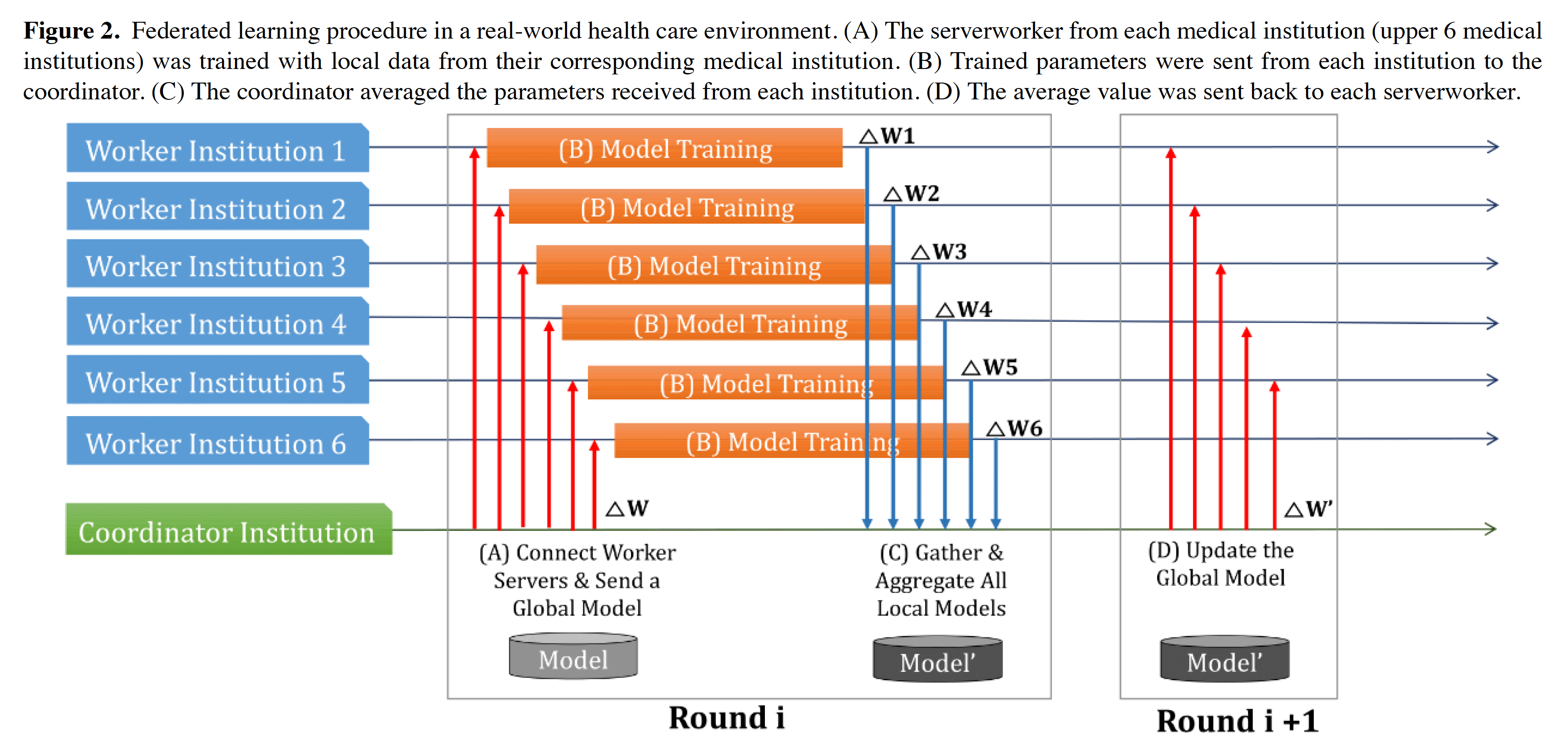
(Background) Federated learning is a decentralized approach to machine learning; it is a training strategy that overcomes medical data privacy regulations and generalizes deep learning algorithms. Federated learning mitigates many systemic privacy risks by sharing only the model and parameters for training, without the need to export existing medical data sets. In this study, we performed ultrasound image analysis using federated learning to predict whether thyroid nodules were benign or malignant. (Objective) The goal of this study was to evaluate whether the performance of federated learning was comparable with that of conventional deep learning. (Methods) A total of 8457 (5375 malignant, 3082 benign) ultrasound images were collected from 6 institutions and used for federated learning and conventional deep learning. Five deep learning networks (VGG19, ResNet50, ResNext50, SE-ResNet50, and SE-ResNext50) were used. Using stratified random sampling, we selected 20% (1075 malignant, 616 benign) of the total images for internal validation. For external validation, we used 100 ultrasound images (50 malignant, 50 benign) from another institution.