Congratulations to Seo-Yeon Choi (Student Researcher, 학부연구생) on Two Papers Accepted to ICCV 2025 Workshops!

We are thrilled to announce that our undergraduate researcher, Seo-Yeon Choi (최서연), has achieved a remarkable accomplishment—two papers have been accepted to workshops at ICCV 2025 Workshops (CVAMD / VADH25)!
Even more exciting, one paper was selected for an oral presentation and the other for a poster presentation. Having two papers accepted at such a prestigious venue as ICCV is a truly outstanding feat, especially for an undergraduate researcher. This is a testament to Seo-Yeon’s dedication, hard work, and innovative research.
Congratulations once again, Seo-Yeon! We look forward to seeing both the oral and poster presentations at ICCV 2025 in Hawaii! 🌺🌴
Patient-Centric Statistical Multi-Modal Fusion for Medical Diagnosis: Integrating DICOM, Radiomics, and Patient Attributes
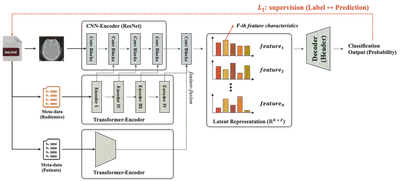
Abstract
Deep learning (DL) has led to substantial progress in medical image analysis, particularly for disease classification. However, the integration of patient-specific attributes, such as age, body mass index (BMI), and lifestyle factors with radiomics and raw imaging data remains a key challenge in the development of personalized diagnostic models. To alleviate this, in this research, we propose a novel multi-modal framework, denoted as Statistically Coherent Network (SCN), which jointly models imaging, radiomic, and patient metadata through a structured multi-space latent representation. SCN facilitates distributional coherence across subpopulations by leveraging a newly devised statistics-based loss in conjunction with a triplet loss, thereby aligning feature distributions among clinically similar cohorts. This statistical alignment using T-test facilitates more interpretable and robust representation learning across heterogeneous patient groups. We evaluate SCN on four clinically diverse tasks, including breast cancer (mammography), obstructive sleep apnea (CT), rotator cuff tear (MRI), and Cormack-Lehane grading (X-ray), and demonstrate the consistent improvements over conventional single-space and multi-modal baselines. The experimental results highlight the importance of explicitly incorporating patient metadata, in terms of multimodal learning, to enhance model generalizability and clinical relevance.
Memory-Guided Personalization for Physician-Specific Diagnostic Inference
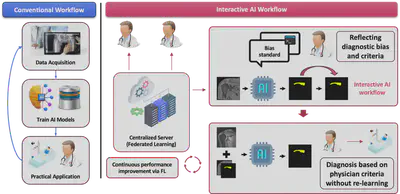
Abstract
Recent advances in deep learning have improved diagnostic precision across medical imaging tasks. However, clinical adoption remains limited due to a mismatch between model outputs and the diverse reasoning styles of physicians. Prior personalization efforts have primarily focused on patient-specific adaptation, overlooking clinician-specific variability. We propose a physician-centric diagnostic framework that supports real-time, adaptive inference tailored to individual clinicians. The system consists of three stages: supervised learning, Human-in-the-Loop guidance, and personalized deployment. Physician feedback is encoded as memory-based priors and reused at inference without retraining, enabling lightweight, end-to-end personalization. We validate our method on detection and segmentation tasks including parathyroid localization, breast cancer segmentation, and rotator cuff tear analysis. Results demonstrated that our model adapts effectively to individual diagnostic styles while maintaining high accuracy in clinical workflows.
Once again, congratulations to Seo-Yeon Choi for this outstanding achievement. Let’s look forward to an inspiring and impactful presentation at ICCV 2025! 🚀🎉